

Next: Introduction
Centre de Recherche Astronomique de Lyon (CRAL),
Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon, Lyon, Cedex 07, 69364 France
E-Mail: fallard@ens-lyon.fr
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy & Centre for Simulational Physics,
University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-2451
Email: yeti@hal.physast.uga.edu
Dept. of Physics, Wichita State University,
Wichita, KS 67260-0032
E-Mail: dra@twsuvm.uc.twsu.edu
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy,
University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-2451
Email: andy@physast.uga.edu
Abstract:
We present opacity sampling model atmospheres, synthetic spectra and
colors for brown dwarfs and very low mass stars in two limiting case
of dust grain formation: 1) inefficient gravitational settling i.e.
the dust is distributed according to the chemical equilibrium
predictions, 2) efficient gravitational settling i.e. the dust forms
and depletes refractory elements from the gas, but their opacity does
not affect the thermal structure. The models include the formation of
over 600 gas phase species, and 1000 liquids and crystals, and the
opacities of 30 different types of grains including corundum
(Al
2O
3), the magnesium aluminum spinel MgAl
2O
4, iron,
enstatite (MgSiO
3), forsterite (Mg
2SiO
4), amorphous carbon,
SiC, and a number of calcium silicates. The models extend from the
beginning of the grain formation regime well into the condensation
regime of water ice (
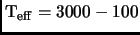
K) and encompasses the range
of
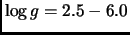
at solar metallicity.
We find that silicate dust grains can form abundantly in the outer
atmospheric layers of red and brown dwarfs with spectral type later
than M8. The greenhouse effects of dust opacities provide a natural
explanation for the peculiarly red spectroscopic distribution of the
latest M dwarfs and young brown dwarfs. The grainless (Cond) models
on the other hand, correspond closely to methane brown dwarfs such as
Gliese 229B. We also recover that the 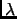 5891,5897Å Na I D
and
5891,5897Å Na I D
and 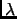 7687,7701Å K I resonance doublets plays a critical
role in T dwarfs where their red wing define the pseudo-continuum from
the I to the Z bandpass.
7687,7701Å K I resonance doublets plays a critical
role in T dwarfs where their red wing define the pseudo-continuum from
the I to the Z bandpass.
low mass stars,brown dwarfs,grains,fundamental parameters


Next: Introduction
Peter Hauschildt
2001-05-23
![]() 5891,5897Å Na I D
and
5891,5897Å Na I D
and ![]() 7687,7701Å K I resonance doublets plays a critical
role in T dwarfs where their red wing define the pseudo-continuum from
the I to the Z bandpass.
7687,7701Å K I resonance doublets plays a critical
role in T dwarfs where their red wing define the pseudo-continuum from
the I to the Z bandpass.